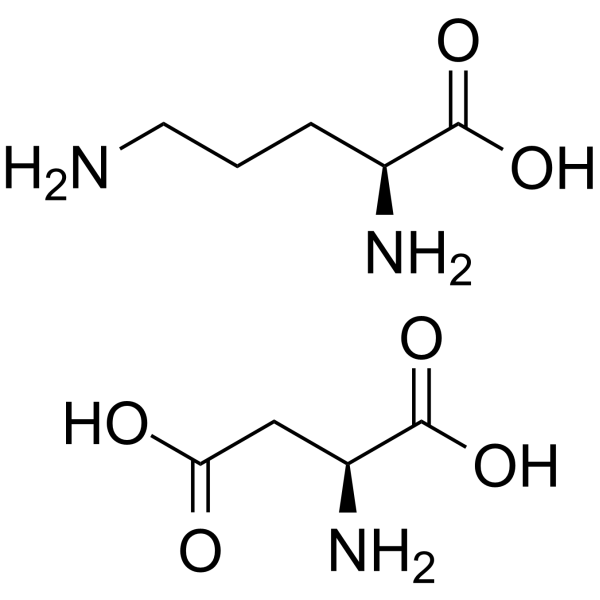
L-Ornithine L-aspartate
CAS No. 3230-94-2
L-Ornithine L-aspartate( Ornithine Aspartate )
Catalog No. M27087 CAS No. 3230-94-2
L-Ornithine L-aspartate lowers blood ammonia concentration and to eliminate symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy associated with liver cirrhosis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameL-Ornithine L-aspartate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionL-Ornithine L-aspartate lowers blood ammonia concentration and to eliminate symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy associated with liver cirrhosis.
-
DescriptionL-Ornithine L-aspartate lowers blood ammonia concentration and to eliminate symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy associated with liver cirrhosis.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsOrnithine Aspartate
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorRIP3
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3230-94-2
-
Formula Weight265.26
-
Molecular FormulaC9H19N3O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 250 mg/mL (942.47 mM)
-
SMILESN[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(O)=O.N[C@@H](CCCN)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Mandal P, et al. RIP3 induces apoptosis independent of pronecrotic kinase activity. Mol Cell. 2014 Nov 20;56(4):481-95.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Buquinolate
Buquinolate is an anticoccidial agent used in poultry, and the medicated chickens can produce higher levels of egg production and gain weight. Buquinolate does not interfere with the formation of immunity against coccidia.
-
Ascr#5
Ascr#5 (asc-ωC3) is a highly conserved ascoside analogue in Cryptococcus hidradii that modulates a variety of responses in Cryptococcus hidradii.
-
Glycyl-L-glutamine m...
Glycyl-L-glutamine monohydrate is an inhibitory neuropeptide derived from beta-endorphin.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


